HEY, ARE YOU AT RISK OF STROKE?
Time is BRAIN
STROKE
In recent years stroke has become more common among people below the age of 60. The elderly, working-age adults and even teenagers can be threatened by stroke depending on a range of factors.
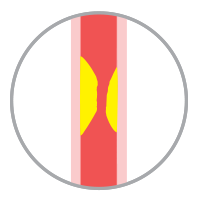
Cerebral Thrombosis
Occurs when a blood clot forms inside a blood vessel within the brain which has been narrowed by the build up of fatty substances (atherosclerosis).
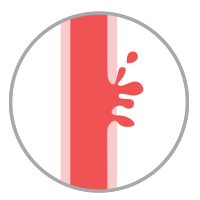
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Occurs when weakened blood vessels rupture and bleed in the brain. The blood accumulates and puts pressure on the surrounding brain tissues, causing damages.
Time is the key to stroke treatments. If any of the FAST symptoms appear, patients need to be in the care of stroke specialists as soon as possible. If reached in a timely manner, modern technology can greatly improve the chances of survival and complete recovery.
“1 million brain cells die every minute after stroke”

F.A.S.T
If any of these symptoms occur, go to the hospital immediately.
F-Face Drooping
Uneven or lopsided smile. Especially with severe headache.
A-Arm Weakness
Cannot raise the arms. Numb limbs. Unsteady walk.
S-Speech Difficulty
Unable to speak or complete a sentence.
STROKE RISK
If the stroke involves clotting in small blood vessels without any bleeding, the patient will be given intravenous r-TPA to dissolve the clot and restore blood flow to the oxygen deprived brain.
Time to hospital: within 4 ½ - 24 hours after symptoms
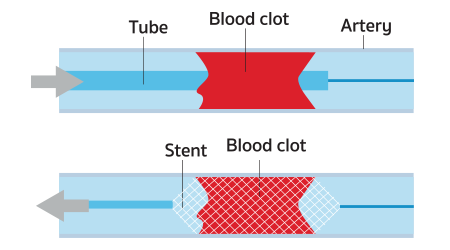
Mechanical thrombectomy with stent retrievers for large-vessel clots. A catheter will be threaded through an artery to remove large blood clots without the need for open brain surgery.
Source : American Heart Association / American Stroke Association, Published Jan, 24,2018
TREATMENT
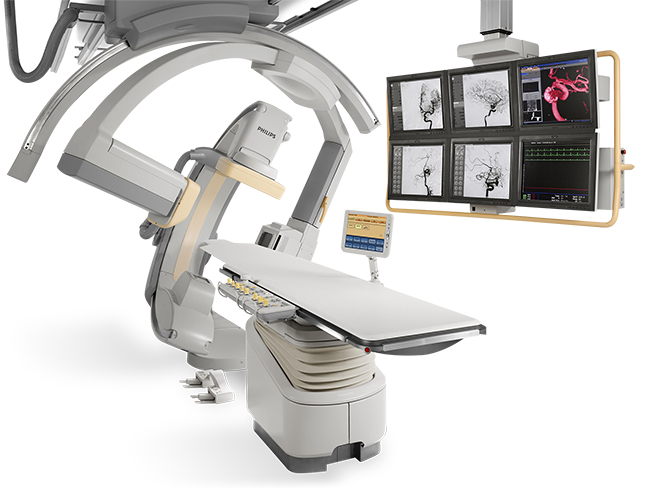
BIPLANE DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY (DSA)
If a major clot is confirmed by a MRI brain scan, contrast material will be injected into the bloodstream to pinpoint its location. The clot will then be removed by a minimally invasive surgical treatment. A small tube (catheter) is inserted through an artery in the groin. The clot is then sucked or dragged out without the need of open brain surgery. A tiny wire tube (stent) might be put in place to prop the artery open. Due to the fragility of these tiny blood vessels, this procedure must be performed by an expert team of interventional radiologists and neurosurgeons.
STROKE REHABILITATION
Early rehabilitation leads to faster brain and muscle function recovery. It can also prevent various complications, such as muscle weakness, respiratory tract infection and deep vein thrombosis. Rehabilitation includes regaining muscle strength and coordination, swallowing, speaking and breathing ability. For the brain itself, rehabilitation involves regaining memory and processing functions and psychological support for mental wellbeing.
STROKE PREVENTION
Time is BRAIN
Bangkok Neuroscience Center

STROKE
In recent years stroke has become more common among people below the age of 60. The elderly, working-age adults and even teenagers can be threatened by stroke depending on a range of factors.

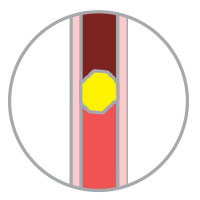
Embolic Stroke
Occurs when a blood clot forms elsewhere (e.g. the heart), travels via the bloodstream, and clogs the tiny blood vessel in the brain.
Cerebral Thrombosis
Occurs when a blood clot forms inside a blood vessel within the brain which has been narrowed by the build up of fatty substances (atherosclerosis).

Hemorrhagic Stroke
Occurs when weakened blood vessels rupture and bleed in the brain. The blood accumulates and puts pressure on the surrounding brain tissues, causing damages.
Time is the key to stroke treatments. If any of the FAST symptoms appear, patients need to be in the care of stroke specialists as soon as possible. If reached in a timely manner, modern technology can greatly improve the chances of survival and complete recovery.
“1 million brain cells die every minute after stroke”

F.A.S.T
If any of these symptoms occur, go to the hospital immediately.
F-Face Drooping
Uneven or lopsided smile. Especially with severe headache.
A-Arm Weakness
Cannot raise the arms. Numb limbs. Unsteady walk.
S-Speech Difficulty
Unable to speak or complete a sentence.
STROKE RISK

If the stroke involves clotting in small blood vessels without any bleeding, the patient will be given intravenous r-TPA to dissolve the clot and restore blood flow to the oxygen deprived brain.
Time to hospital: within 4 ½ - 24 hours after symptoms
Mechanical thrombectomy with stent retrievers for large-vessel clots. A catheter will be threaded through an artery to remove large blood clots without the need for open brain surgery.
Source : American Heart Association / American Stroke Association, Published Jan, 24,2018
TREATMENT

BIPLANE DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY (DSA)
If a major clot is confirmed by a MRI brain scan, contrast material will be injected into the bloodstream to pinpoint its location. The clot will then be removed by a minimally invasive surgical treatment. A small tube (catheter) is inserted through an artery in the groin. The clot is then sucked or dragged out without the need of open brain surgery. A tiny wire tube (stent) might be put in place to prop the artery open. Due to the fragility of these tiny blood vessels, this procedure must be performed by an expert team of interventional radiologists and neurosurgeons.

STROKE REHABILITATION
Early rehabilitation leads to faster brain and muscle function recovery. It can also prevent various complications, such as muscle weakness, respiratory tract infection and deep vein thrombosis. Rehabilitation includes regaining muscle strength and coordination, swallowing, speaking and breathing ability. For the brain itself, rehabilitation involves regaining memory and processing functions and psychological support for mental wellbeing.
STROKE PREVENTION
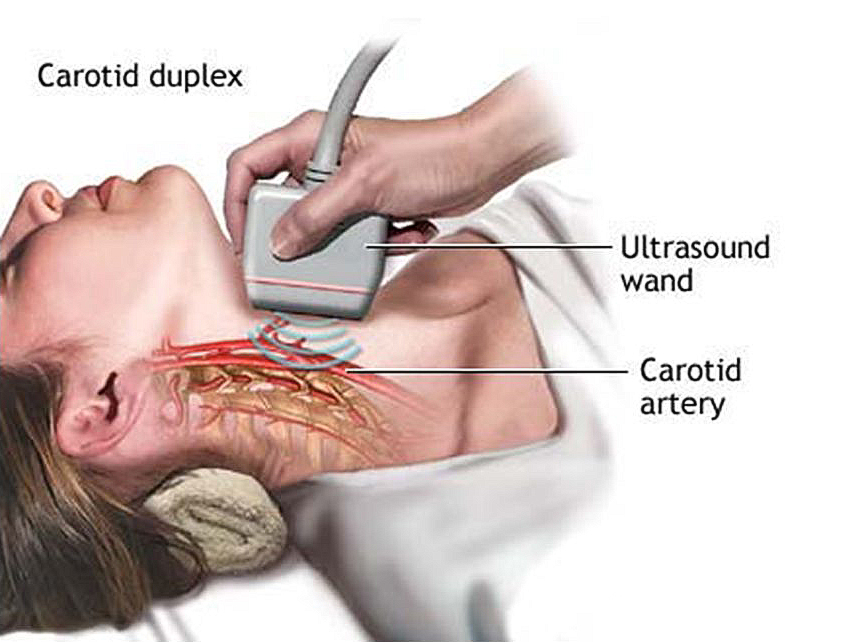
Strokes can happen to anyone, regardless of age or gender, and may even reoccur. Those with risk factors need to start a healthier lifestyle: balanced diet, regular exercise and an annual check-up with special attention to glucose levels, blood pressure and heart activity. Family history of aneurysms, ischemic heart disease and paralysis/paresis could also increase the risks. A carotid ultrasound can identify narrowed carotid arteries, allowing your doctor to prescribe stroke prevention measures.